Earwax impaction
OVERVIEW
What is earwax?
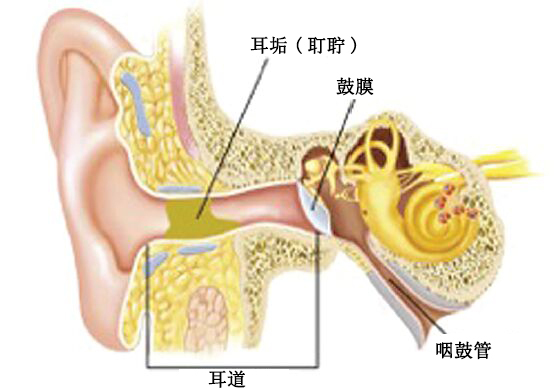
Earwax, commonly known as "earwax," is a pale yellow, sticky secretion produced by the ceruminous glands in the skin of the cartilaginous portion of the external ear canal. After drying in the air, it forms thin flakes, but some earwax remains sticky like grease, commonly referred to as "oily earwax."
What is cerumen impaction?
Earwax protects the skin and mucous membrane of the external ear canal and adheres to foreign substances (such as insects, dust, etc.). Normally, through movements like chewing or opening the mouth, earwax can naturally fall out or be expelled. If earwax accumulates and forms a mass, blocking the external ear canal, it is called cerumen impaction.
After cerumen impaction forms, it can affect hearing or trigger ear infections, leading to hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, or reflexive coughing. When exposed to water, it may swell and further impair hearing, irritate the skin of the external ear canal, causing localized erosion, swelling, pain, or even pus discharge.
Is cerumen impaction common?
Cerumen impaction is relatively common, but there are currently no precise statistics on its incidence rate.
What types of cerumen impaction are there?
There is no clear classification for cerumen impaction, but earwax itself can be divided into dry and wet types.
Is cerumen impaction hereditary?
Currently, there is no direct literature proving its correlation with heredity.
However, a Chinese study in the 1990s analyzed diagnosed patients and found that if one parent had the condition, half of their children might also develop it, with no difference in incidence between genders. Additionally, many patients with this condition also had axillary osmidrosis.
Thus, it is suspected that there may be a hereditary component. With advancements in science, this will likely be further studied and explained.
SYMPTOMS
What are the common symptoms of cerumen impaction?
After cerumen impaction forms, patients may feel a blockage in the ear, experience hearing loss, or have recurring ear infections, tinnitus, dizziness, or reflex coughing. When exposed to water, the impaction may swell, leading to further hearing loss, irritation of the external ear canal skin, causing local erosion, swelling, pain, or even pus discharge.
Where does cerumen impaction commonly occur?
Cerumen impaction usually occurs in the external ear canal.
What serious complications can cerumen impaction cause?
Once cerumen impaction forms, it can affect hearing or trigger ear infections.
CAUSES
What causes cerumen impaction?
Cerumen impaction is generally caused by either excessive production or impaired expulsion.
-
Excessive production is often seen in cases of ear inflammation or dust irritation;
-
Impaired expulsion is mostly due to narrow ear canals, foreign objects, muscle relaxation in the elderly, or weak jaw movement.
Who is prone to cerumen impaction?
Most people have dry, flaky earwax, which tends to expel naturally.
-
However, some individuals produce excessive earwax that is thick, soft, and yellowish, commonly known as "wet earwax." Their earwax tends to clump together and is difficult to expel, eventually blocking the ear canal.
-
Swimming enthusiasts, whose ears are frequently exposed to water or damp environments, or who develop recurrent ear infections due to such conditions, are also prone to cerumen impaction.
DIAGNOSIS
How is cerumen impaction diagnosed?
If you experience symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus, ear pain, or even dizziness in daily life, and observe brown or yellowish blockages in the ear canal, you should visit an ENT specialist for further examination and diagnosis.
What tests are needed for cerumen impaction?
An otoscopy is usually sufficient for diagnosis.
However, some ear conditions, such as cholesteatoma or ear canal scabies, may resemble cerumen impaction. If these conditions are suspected, the doctor may perform additional tests like hearing assessments for confirmation.
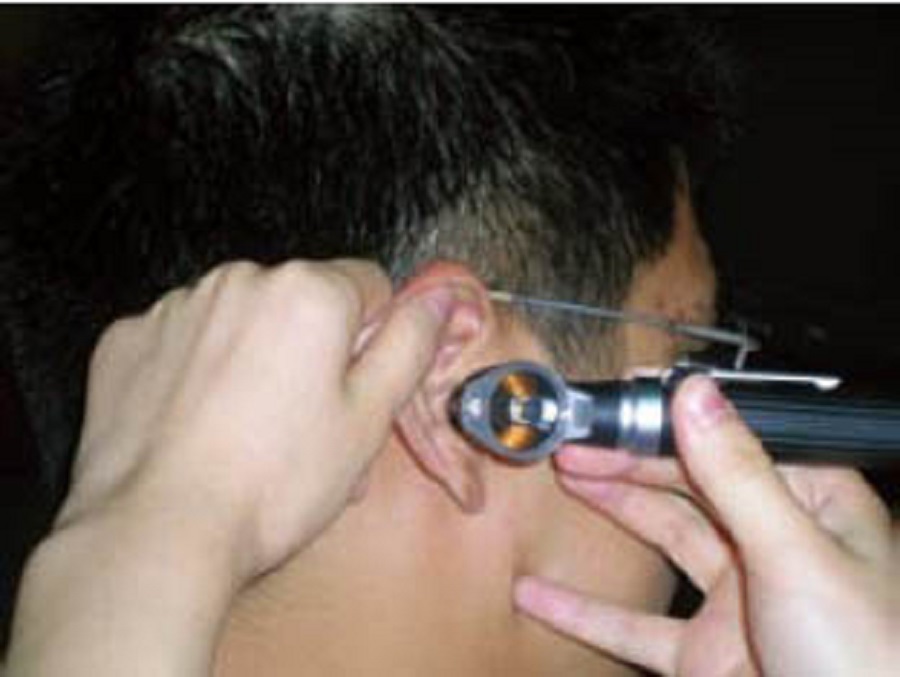
What is an otoscopy for cerumen impaction?
Otoscopy: This procedure involves visually examining the ear canal to check for cerumen impaction, assess the nature of the earwax, the degree of blockage, and its relationship with the ear canal. (See image below)
Are cerumen impaction and ear canal cholesteatoma the same condition?
No, they are different.
Ear canal cholesteatoma is caused by the accumulation of desquamated epithelial cells containing cholesterol crystals due to various factors. Excessive buildup can block the ear canal.
Causes of cholesteatoma include ear canal narrowing, trauma (e.g., repeated ear cleaning leading to scratches), obstruction, or infection. Symptoms often include ear fullness, hearing loss, sensorineural deafness, and ear pain, which may overlap with cerumen impaction.
Otoscopy may sometimes show a mass resembling earwax, leading to confusion. However, cholesteatoma contains epithelial debris (appearing white, shiny, and tough, resembling fish skin) and produces enzymes that erode ear canal bones. Pathological examination reveals epithelial cells, distinguishing it from cerumen impaction.
TREATMENT
Which department should I visit for cerumen impaction?
Otolaryngology (ENT) department.
Can cerumen impaction resolve on its own?
It is generally difficult to expel naturally and usually requires professional removal.
How is cerumen impaction treated?
For hard, difficult-to-remove cerumen, 5% sodium bicarbonate solution can be instilled into the ear canal 4-6 times daily. After softening, it can be removed using alligator forceps, a cerumen hook, suction, or ear canal irrigation.
Does cerumen impaction require hospitalization?
Most patients with simple cerumen impaction do not require hospitalization.
What precautions should be taken during cerumen removal?
-
Ear irrigation is contraindicated for patients with perforated eardrums (e.g., acute/chronic suppurative otitis media) or ear canal stenosis;
-
Avoid attempting self-removal with cotton swabs or hard objects, as this may cause ear canal injury or even eardrum perforation with permanent hearing damage;
-
Keep the ear clean and dry after removal;
-
Patients may temporarily experience hypersensitivity to high-pitched sounds post-removal - loosely placing sterile cotton at the ear opening for half to one day may help.
What post-treatment care is needed for cerumen impaction?
After removal, maintain dry and clean ear canals.
Is follow-up required after cerumen impaction treatment?
Monthly follow-up visits for the first three months after ear irrigation are recommended.
Can cerumen impaction be completely cured?
Complete removal typically results in full recovery.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What precautions should patients with cerumen impaction take in daily life?
-
Reduce fat intake in the diet.
-
If there is ear canal inflammation, actively treat external ear canal inflammation.
PREVENTION
Can earwax impaction be prevented? Can I clean my ears?
Earwax impaction can be prevented.
-
Maintaining ear canal hygiene in daily life, avoiding infections, preventing water from entering the ears, and actively treating ear canal inflammation if present are key to preventing recurrence.
-
Avoid cleaning ears improperly: Using unsterilized sharp tools may cause damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Repeated long-term irritation of the external ear canal can even lead to abnormal tissue proliferation and trigger external auditory canal papilloma.